How to operate a drone is a question many ask, bridging the gap between technological marvel and practical application. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the various types and their unique control mechanisms to mastering aerial photography and adhering to crucial safety and legal regulations. We’ll explore pre-flight checks, navigation techniques, and maintenance procedures, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently pilot your own drone.
This comprehensive exploration covers everything from selecting the right drone for your needs to understanding and applying advanced flight techniques. We’ll navigate the complexities of airspace regulations and provide practical troubleshooting advice for common issues. Whether you’re a beginner or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this guide offers a clear and accessible path to mastering the art of drone piloting.
Drone Types and Their Operation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore the key differences between multirotor, fixed-wing, and single-rotor drones, examining their control interfaces, specific models, and flight capabilities.
Multirotor, Fixed-Wing, and Single-Rotor Drone Differences
Multirotor drones, commonly known as quadcopters or hexacopters, utilize multiple rotors for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and maneuverability. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, require a runway for takeoff and landing, offering longer flight times and ranges. Single-rotor drones, or helicopters, combine vertical lift with directional control through a single rotor and a tail rotor for stability. Operational differences stem primarily from their flight dynamics and control mechanisms.
Drone Control Interfaces
Drone control interfaces vary significantly across models. Many utilize handheld transmitters with joysticks for controlling throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Some advanced models integrate smartphone or tablet apps for flight control and camera operation, offering features like waypoint navigation and automated flight modes. Others may use specialized software interfaces for professional applications requiring precise control and data logging.
Specific Drone Models and Operational Features
Examples include the DJI Mavic 3, known for its high-resolution camera and obstacle avoidance; the Autel EVO II, renowned for its long flight time and dual-sensor camera system; and the Parrot Anafi, praised for its compact size and foldable design. Each model offers unique operational features such as different camera capabilities, flight modes, and intelligent flight functions.
Flight Characteristics Comparison, How to operate a drone

| Drone Type | Speed (km/h) | Range (km) | Payload Capacity (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multirotor (DJI Mavic 3) | 72 | 30 | 0.9 |
| Fixed-Wing (3DR Solo) | 100 | 80 | 1.5 |
| Single-Rotor (DJI Matrice 300 RTK) | 72 | 15 | 2.7 |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to strict safety protocols are paramount to ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This section Artikels essential steps for pre-flight inspection, safety procedures, emergency protocols, and handling unexpected situations.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves visually inspecting the drone’s body, propellers, battery, camera, and other components for any damage or defects. Checking the battery level, GPS signal strength, and controller connectivity is also crucial. Confirming the drone’s firmware is up-to-date and reviewing weather conditions are equally important steps.
Safety Protocols
Before flight, ensure you have obtained any necessary permits or licenses and are aware of local airspace restrictions. During flight, maintain visual line of sight with the drone and avoid flying near people, buildings, or other obstacles. After flight, safely land the drone and power it off, storing it in a protective case.
Pre-Flight Checklist Flowchart
The pre-flight checklist can be visualized as a flowchart, starting with a power-on self-test, moving to visual inspection, battery check, GPS signal verification, and finally, confirmation of flight conditions. Any issue encountered leads to a troubleshooting step before proceeding. Successful completion allows for flight initiation.
Emergency Procedures
Emergency procedures include knowing how to utilize the return-to-home (RTH) function in case of signal loss or low battery. Understanding how to perform an emergency landing and the procedures for retrieving a crashed drone are also essential. In case of malfunctions, attempting a controlled descent and power-off are vital actions.
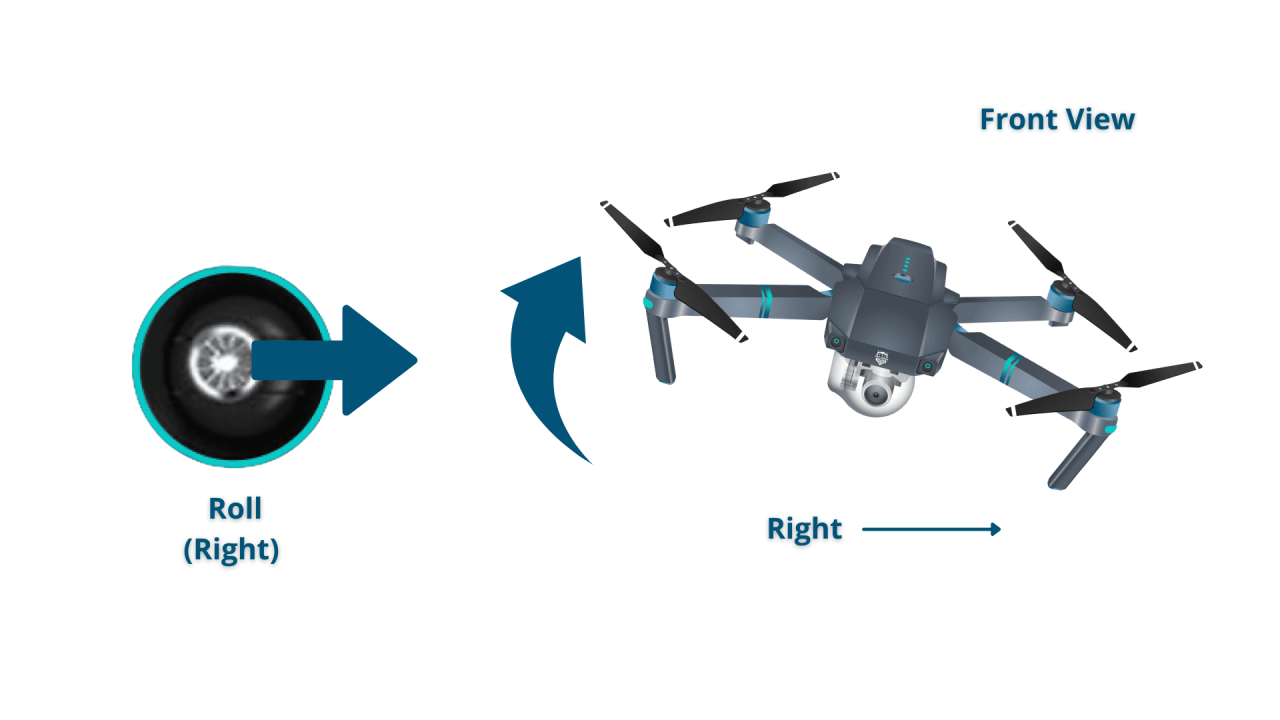
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Effective drone operation hinges on understanding the drone controller and navigation systems. This section details the functions of control sticks, explains altitude hold, GPS navigation, return-to-home (RTH) functions, and provides strategies for overcoming common navigation challenges and planning flight paths.
Drone Controller Functions
A typical drone controller has two joysticks. The left joystick typically controls altitude and direction, while the right joystick manages pitch and yaw (rotation). Buttons and switches on the controller provide access to various functions like camera control, flight modes, and return-to-home. Understanding the responsiveness and dead zones of each control is vital for precise maneuvers.
Altitude Hold, GPS Navigation, and RTH
Altitude hold maintains a consistent altitude, simplifying flight and reducing pilot workload. GPS navigation allows for precise positioning and waypoint navigation, enabling the drone to follow a pre-planned flight path. RTH automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point in case of signal loss or low battery, enhancing safety.
Navigation Challenges and Solutions
Common navigation challenges include GPS signal interference, strong winds, and obstacles. Solutions involve selecting appropriate flight locations with clear GPS signals, avoiding windy conditions, and utilizing obstacle avoidance features (if available). Careful flight planning and pilot skill are crucial for mitigating these challenges.
Waypoint Navigation
Planning a drone flight path using waypoint navigation involves setting a series of waypoints on a map or using pre-programmed flight paths. The drone autonomously navigates between these waypoints, allowing for complex flight patterns and consistent image capture for tasks such as aerial photography or surveying. This requires familiarity with the drone’s software and flight planning tools.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section explores techniques for stable images, optimal camera adjustments, camera modes, and composition tips for compelling aerial shots.
Capturing Stable and Sharp Aerial Images
Stable images require smooth drone operation, minimizing sudden movements. Utilizing features like gimbal stabilization and understanding the effects of wind on image stability are crucial. Proper focus and exposure settings are also essential for sharpness.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for optimal results in different lighting conditions. Higher ISO settings are useful in low light, but may increase noise. Slower shutter speeds require stable conditions to avoid motion blur, while faster speeds freeze motion. Aperture controls depth of field.
Camera Modes
Different camera modes such as photo, video, and timelapse offer diverse creative options. Photo mode captures single images, video mode records continuous footage, and timelapse mode creates time-lapse sequences from a series of still images, compressing time to show changes over an extended period.
Tips for Composing Aerial Shots

Composition techniques include the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry. Consider the angle of the shot, the background, and the subject matter to create visually appealing and impactful images. Experimenting with different perspectives and compositions is key to finding unique and compelling aerial shots.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are vital for ensuring optimal drone performance and longevity. This section Artikels essential maintenance tasks, common malfunctions, troubleshooting steps, and a maintenance checklist.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and ensure safe and responsible flying. Ultimately, responsible operation hinges on understanding both the technical aspects and the legal framework governing drone usage.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance includes inspecting propellers for damage, cleaning the drone body and sensors, checking and calibrating the compass and IMU, and ensuring all screws and fasteners are secure. Proper battery care, including storage and charging, is crucial for extending battery life.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Common malfunctions include motor failures, GPS signal loss, battery issues, camera malfunctions, and software glitches. Understanding potential causes, such as physical damage, software bugs, or environmental factors, is important for effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components, identifying the source of the problem, and implementing appropriate solutions. This may involve replacing damaged parts, updating firmware, recalibrating sensors, or seeking professional assistance if the issue is complex.
Drone Maintenance Checklist
A regular drone maintenance checklist should include visual inspections, component checks, cleaning, firmware updates, sensor calibrations, and battery care. A schedule for these tasks ensures the drone remains in optimal condition and minimizes the risk of malfunctions.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to local drone regulations is crucial for responsible and legal drone operation. This section highlights the importance of compliance, airspace restrictions, permit acquisition, and the consequences of violations.
Importance of Adhering to Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location and are designed to ensure public safety and prevent interference with other airspace users. Ignoring these regulations can lead to fines, legal action, and potential harm.
Airspace Restrictions
Airspace restrictions include no-fly zones around airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. These restrictions are often mapped using online resources and must be checked before each flight. Understanding airspace classifications is essential.
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
Depending on the drone’s size, purpose of use, and location, obtaining necessary permits or licenses may be required. The process for obtaining these permissions varies depending on local regulations and should be researched in advance.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and understanding the controls; for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and regulations.
Common Violations and Consequences
Common violations include flying in restricted airspace, exceeding altitude limits, and operating without necessary permits. Consequences can range from warnings and fines to equipment confiscation and legal prosecution. Responsible drone operation includes full compliance with all regulations.
Advanced Drone Operations
Advanced drone operations involve utilizing features like obstacle avoidance and autonomous flight modes, performing complex maneuvers, and understanding associated safety considerations. This section explores these advanced capabilities.
Obstacle Avoidance and Autonomous Flight
Obstacle avoidance systems utilize sensors such as cameras, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors to detect obstacles and adjust the drone’s flight path to avoid collisions. Autonomous flight modes allow the drone to perform pre-programmed maneuvers or follow a predefined path without constant pilot input. These systems enhance safety and efficiency but require careful understanding of their limitations.
Complex Maneuvers
Complex maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, are possible with some drone models, but require significant skill and careful consideration of safety. These maneuvers should only be attempted in open, safe areas with ample space to avoid obstacles or collisions. Understanding the drone’s capabilities and limitations is essential.
Safety Considerations for Advanced Operations
Safety considerations for advanced operations include selecting suitable environments for complex maneuvers, ensuring sufficient battery life, maintaining awareness of surrounding conditions, and having a plan for handling unexpected situations. Always prioritize safety over attempting advanced features beyond one’s skill level.
Obstacle Avoidance System Visualization
Imagine a sphere of sensors surrounding the drone, constantly scanning for objects. When an object is detected within a certain range, the drone’s flight controller processes this information and adjusts the drone’s flight path to avoid the obstacle, either by changing direction or altitude. The system’s effectiveness depends on the type and range of the sensors used and environmental conditions.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. From understanding the mechanics of flight to navigating complex airspace regulations, this guide has provided a solid foundation for safe and responsible drone piloting. By consistently applying the pre-flight checklists, adhering to safety protocols, and continually honing your piloting skills, you can confidently explore the limitless possibilities of aerial perspectives.
Remember to always prioritize safety and legal compliance in your drone adventures.
Essential FAQs
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring intuitive controls and automated features. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features before making a purchase.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging. Generally, it’s best to avoid fully depleting the battery and to charge it after each flight session.
What happens if I lose GPS signal during flight?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone and be prepared to manually control it if necessary.
Can I fly my drone in the rain?
No. Operating a drone in rain or other adverse weather conditions can severely damage the electronics and is highly unsafe. Always check weather forecasts before flying.
